METHOD 24A - DETERMINATION OF VOLATILE MATTER CONTENT AND DENSITY OF PUBLICATION ROTOGRAVURE INKS AND RELATED PUBLICATION ROTOGRAVURE COATINGS
8.0 Sample Collection,
Preservation, Storage, and Transport.
9.0 Quality Control.
[Reserved]
10.0 Calibration and
Standardization. [Reserved]
11.2 Ink or Related
Coating Density.
12.0 Calculations and
Data Analysis.
13.0 Method
Performance. [Reserved]
14.0 Pollution
Prevention. [Reserved]
15.0 Waste Management.
[Reserved]
17.0 Tables, Diagrams,
Flowcharts, and Validation Data. [Reserved]
1.0 Scope and Application.
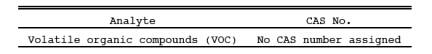
1.1 Analytes.
1.2 Applicability.
This method is applicable for the determination of the VOC content and density
of solvent-borne (solvent-reducible) publication rotogravure inks and related
publication rotogravure coatings.
2.0 Summary of Method.
2.1 Separate
procedures are used to determine the VOC weight fraction and density of the ink
or related coating and the density of the solvent in the ink or related
coating. The VOC weight fraction is determined by measuring the weight loss of
a known sample quantity which has been heated for a specified length of time at
a specified temperature. The density of both the ink or related coating and
solvent are measured by a standard procedure. From this information, the VOC
volume fraction is calculated.
3.0 Definitions. [Reserved]
4.0 Interferences. [Reserved]
5.0 Safety.
5.1 Disclaimer.
This method may
involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This test method does
not purport to address all of the safety problems associated with its use. It
is the responsibility of the user of this test method to establish appropriate
safety and health practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to performing this test method.
5.2 Hazardous Components.
Some of the compounds
that may be contained in the inks or related coatings analyzed by this method
may be irritating or corrosive to tissues or may be toxic. Nearly all are fire
hazards. Appropriate precautions can be found in reference documents, such as
Reference 6 of Section 16.0.
6.0 Equipment and Supplies.
The following
equipment and supplies are required for sample analysis:
6.1 Weighing Dishes.
Aluminum foil, 58 mm (2.3 in.) in diameter by 18 mm (0.7 in.) high, with a flat
bottom. There must be at least three weighing dishes per sample.
6.2 Disposable
Syringe. 5 ml.
6.3 Analytical
Balance. To measure to within 0.1 mg.
6.4 Oven. Vacuum oven
capable of maintaining a temperature of 120 ± 2 ûC (248 ± 4 ûF) and an absolute
pressure of 510 ± 51 mm Hg (20 ± 2 in. Hg) for 4 hours. Alternatively, a forced draft oven capable of maintaining
a temperature of 120 ± 2 ûC (248 ± 4 ûF) for 24 hours.
6.5 The equipment and
supplies specified in ASTM D 1475- 60, 80, or 90 (incorporated by reference -
see ¤60.17).
7.0 Reagents and Standards.
7.1 The reagents and standards
specified in ASTM D 1475-60, 80, or 90 are required.
8.0 Sample Collection, Preservation, Storage, and Transport.
8.1 Follow the sample
collection, preservation, storage, and transport procedures described in
Reference 4 of Section 16.0.
9.0 Quality Control. [Reserved]
10.0 Calibration and Standardization. [Reserved]
11.0 Analytical Procedure.
Additional guidance
can be found in Reference 5 of Section 16.0.
11.1 VOC Weight Fraction.
Shake or mix the ink
or related coating sample thoroughly to assure that all the solids are
completely suspended. Label and weigh to the nearest 0.1 mg a weighing dish and
record this weight (Mx1). Using a 5 ml syringe, without a needle,
extract an aliquot from the ink or related coating sample. Weigh the syringe
and aliquot to the nearest 0.1 mg and record this weight (Mcy1). Transfer 1 to 3 g of the aliquot to the tared
weighing dish. Reweigh the syringe and remaining aliquot to the nearest 0.1 mg
and record this weight (Mcy2). Heat the weighing dish with the transferred
aliquot in a vacuum oven at an absolute pressure of 510 ± 51 mm Hg (20 ± 2 in.
Hg) and a temperature of 120 ± 2 ûC (248 ± 4 ûF) for 4 hours. Alternatively,
heat the weighing dish with the transferred aliquot in a forced draft oven at a
temperature of 120 ± 2 ûC for 24 hours. After the weighing dish has cooled,
reweigh it to the nearest 0.1 mg and record the weight (Mx2). Repeat this procedure two times for each ink or related coating
sample, for a total of three samples.
11.2 Ink or Related Coating Density.
Determine the density
of the ink or related coating (Dc) according to the
procedure outlined in ASTM D 1475. Make a total of three determinations for
each ink or related coating sample. Report the ink or related coating density
as the arithmetic average (øDc) of the three
determinations.
11.3 Solvent Density.
Determine the density
of the solvent (Do) according to the procedure outlined in ASTM D
1475. Make a total of three determinations for each ink or related coating
sample. Report the solvent density as the arithmetic average (øDo) of the three determinations.
12.0 Calculations and Data Analysis.
12.1 VOC Weight
Fraction. For each determination, calculate the volatile organic content weight
fraction (Wo) using the following equation: Make a total of
three determinations. Report the VOC weight fraction as the arithmetic average
(øWo) of the three determinations.
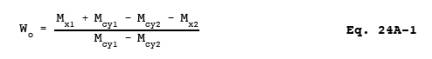
12.2 VOC Volume
Fraction. Calculate the volume fraction volatile organic content (Vo) using the following equation:

13.0 Method Performance. [Reserved]
14.0 Pollution Prevention. [Reserved]
15.0 Waste Management. [Reserved]
16.0 References.
1. Standard Test
Method for Density of Paint, Varnish, Lacquer, and Related Products. ASTM Designation
D 1475.
2. Teleconversation.
Wright, Chuck, Inmont Corporation with Reich, R., A., Radian Corporation.
September 25, 1979, Gravure Ink Analysis.
3. Teleconversation.
Oppenheimer, Robert, Gravure Research Institute with Burt, Rick, Radian Corporation,
November 5, 1979, Gravure Ink Analysis.
4. Standard Procedure
for Collection of Coating and Ink Samples for Analysis by Reference Methods 24
and 24A. EPA-340/1-91-010. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Stationary
Source Compliance Division, Washington, D.C. September 1991.
5. Standard Operating
Procedure for Analysis of Coating and Ink Samples by Reference Methods 24 and
24A. EPA-340/1-91-011. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Stationary Source
Compliance Division, Washington, D.C. September 1991.
6. Handbook of
Hazardous Materials: Fire, Safety, Health. Alliance of American Insurers.
Schaumberg, IL. 1983.
17.0 Tables, Diagrams, Flowcharts, and Validation Data. [Reserved]